Internet-of-things and industry 4.0 has led to the proliferation of an ever increasing number of connected devices, giving rise to problems linked to the security of corporate data. Korenix, a leading manufacturer of ethernet switches and routers for industrial applications, developed "Cyber Security" features that meet IEC-62443-4-2 and provide more safety and reliable network infrastructure. Below we will analyze two important technologies aimed at improving network security: DHCP Snooping and Dynamic ARP Inspection
Cyber Attacks to DHCP infrastructure: Today DHCP is available onmost industrial network devices. However, DHCP is not secure and the operation can be simplyinterrupted without advanced cyberattack skills. One of the most common attack isDHCP spoofing, a cyberattack issued froma rogue DHCP server which scramblesa normal DHCP transaction
When a DHCP client asks for an IP address by broadcasting a DISCOVER message to find a DHCP server on the LAN, the request can reach a legitimate server and a rogue server as well. Both serverssend their OFFERmessage with an IP address. However, the client only takes the one which returns first. If the client accepts the IP address from the rogue server. The system is hacked.
Defense against DHCP attacks: DHCP Snooping is a network security feature implemented on switches or routers aiming to protect the DHCP infrastructure. As indicated by its name, it snoops DHCP messages, checks if the messages are sent from trusted servers, validates the payload, forwards correct messages and discards incorrect ones. It ensures that network configurations are given correctly.
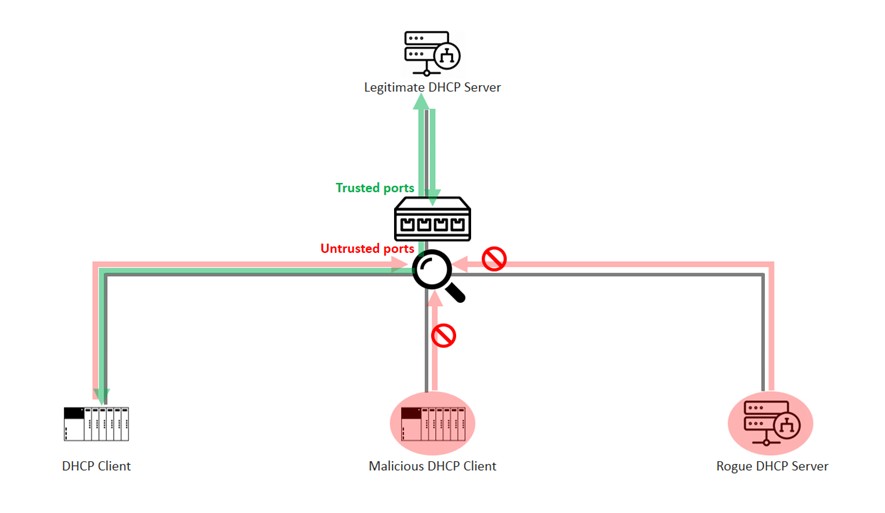
Network switches or routers with DHCP Snooping make two big differences to a DHCP infrastructure. Firstly, the DHCP messages are picked up, validated and filtered. Secondly, valid messages are only forwarded to trusted servers and only the configurations come from trusted sources are given to clients. This greatly reduces the issue of DHCP attacks.
In conclusion, DHCP protocol is convenient and widely used in industrial applications. However, it is not secure by nature and its vulnerabilities demand immediate attention. The network security feature, DHCP Snooping, is critical to protect those industrial automation and control systems relying on DHCP services.
Attacks to Address Resolution Protocol (ARP): ARP is a fundamental protocol of IP networking. It is required by all network devices to resolve the IP-to-MAC mapping before starting IP communication. However, ARP is not secure and is not protected by any cyber security mechanisms. A malicious user can send spoofed ARP messages to overwrite an IP-to-MAC mapping.This is known as ARP Spoofing.
Attackers very often use ARP Spoofing to redirect traffic as starting point of other attacks, such as, inspecting the content (spying), or modifying the content before forwarding to the actual destination (man-in-the-middle attack), or taking over the role of default gateway to stop communication (deny-of-service attack).
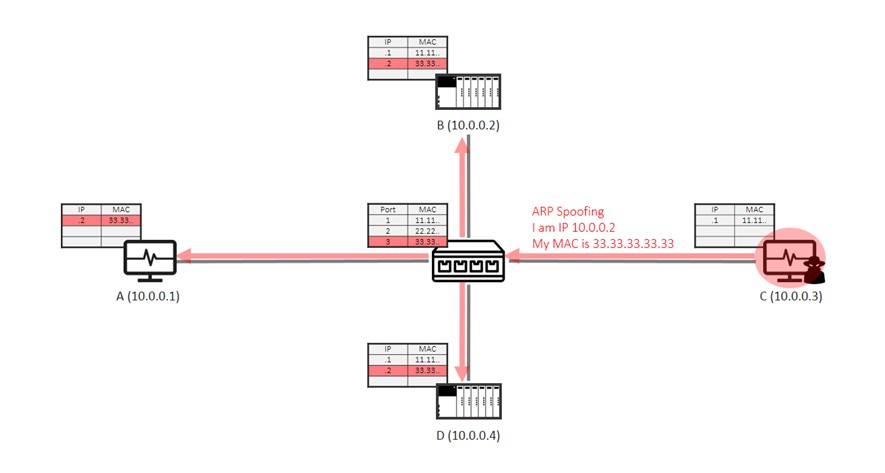
The below diagram shows a scenario how easy Host C (10.0.0.3, on switch port 3) grabs the IP packets aiming at Host B by ARP Spoofing. Host C broadcasts a fabricated IP-to-MAC mapping (B’s IP address and C’s MAC address), which overwrites the correct mapping cached in all hosts’ ARP table and the switch’s MAC address table.This attack makes subsequent IP packets that target at Host B be forwarded to Host C.
Prevent ARP Attacks: Dynamic ARP Inspection is a network security feature on advanced Ethernet switches or routers. It intercepts ARP messages, validates IP-to-MAC mappings, forwards valid messages and discards invalid ones. It ensures that only correct IP-to-MAC mapping can come into the network, thus prevents ARP spoofing attacks.
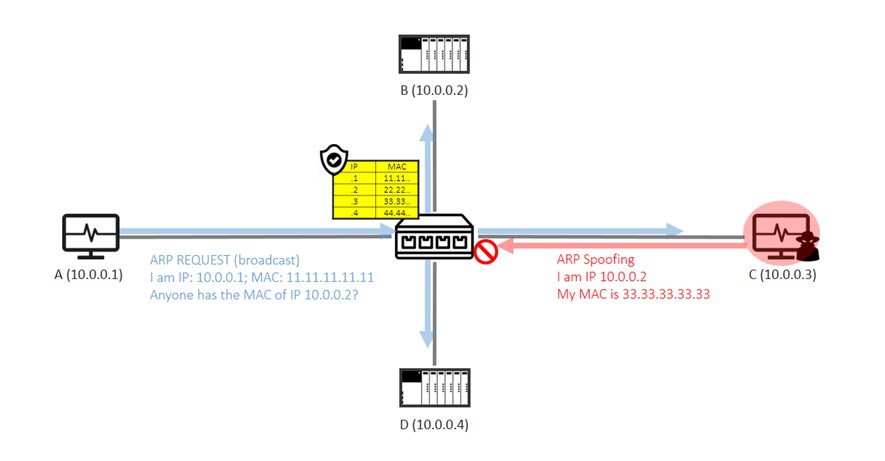
The diagram below shows how Dynamic ARP Inspection works: Host A sends an ARP request. The switch intercepts and compares the source IP and the source MAC address of the message to a trusted database, which can be either created manually or by DHCP snooping. The message is forwarded only if the mapping is correct. The ARP spoofing attack from Host C is dropped because the IP-to-MAC mapping does not match.
In conclusions, IP address must be resolved into MAC address before a message can be sent. The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), serving for this purpose, is a fundamental of IP networking. However, it is not secure and the attacks to its vulnerabilities threaten the very basic operation of modern industrial data communication. The network security feature, Dynamic ARP Inspection, plays an important role to defend against the ARP attacks.
The DHCP Snooping and Dynamic ARP Inspection features are implemented on Korenix's 19" rackmount switches and will be soon implemented on the DIN rail ethernet switch family.























